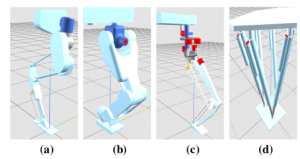
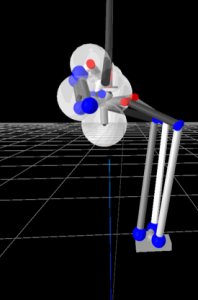
Le projet s’articule essentiellement autour de la bibliothèque de modélisation robotique Pinocchio [1], et particulièrement autour de sa manière de modéliser les contacts. se travaille s’appuie aussi sur l’état de l’art autour des robots humanoïdes existant. 5 robots humanoïdes différents ont été identifiés comme décrivant l’état de l’art de la littérature actuelle :
– Digit [2] Robot série parallèle avec des jambes s’inspirant des jambes d’oiseau. Ce robot est plutôt dynamique, et commence à être utilisés en substituent des humains dans des entrepôts pour des taches de manutention
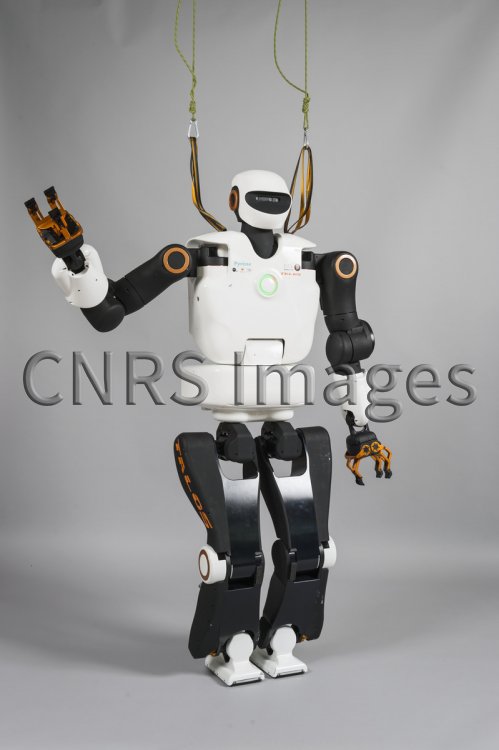
– Talos [3] Robot sériel, massif et lent. Il a des jambes s’inspirant de jambe humaine et est conçu pour porter des charges lourdes. Il est représentatif de l’ensemble des architectures sérielles de jambe de robot existant d’un point de vue cinématique de la jambe.
-Kangaroo [4], Un robot série parallèle d’une grande complexité. Assez unique dans la littérature , il reprend néanmoins des concepts d’actionnement d’autre robot, tels que la hanche ressemblant à la hanche de Tello [6]
-WL16 [5], Robot entièrement parallèle. Bien que parallèle, l’architecture n’est pas d’une grande complexité. Il s’agit de la seule jambe de robot à 6ddl entièrement parallèle identifié dans la littérature.
-Disney Bipedal Robot [6], un robot série parallèle disposant d’une architecture originale. L’utilisation de mécanisme 5 barres pour la transmission du mouvement aux pieds ressemble au robot Atrias [8].
L’approche privilégiée pour optimiser l’architecture de jambes est une approche de co-design [9], De plus l’algorithme d’optimisation qui est privilégié est l’algorithme génétique NSGAIII, qui donne de bons résultats pour de l’optimisation d’architectures mécaniques [10].
[1] Carpentier, J., Budhiraja, R., & Mansard, N. (2021, July). Proximal and sparse resolution of constrained dynamic equations. In Robotics: Science and Systems 2021
[2] G. A. Castillo, B. Weng, W. Zhang and A. Hereid, « Robust Feedback Motion Policy Design Using Reinforcement Learning on a 3D Digit Bipedal Robot, » 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 2021, pp. 5136-5143, doi: 10.1109/IROS51168.2021.9636467
[3] O. Stasse et al., « TALOS: A new humanoid research platform targeted for industrial applications, » 2017 IEEE-RAS 17th International Conference on Humanoid Robotics (Humanoids), Birmingham, UK, 2017, pp. 689-695, doi: 10.1109/HUMANOIDS.2017.8246947 lien ?
[4] Adria Roig, Sai Kishor Kothakota, Narcis Miguel, Pierre Fernbach, Enrico Mingo Hoffman, et al.. On the Hardware Design and Control Architecture of the Humanoid Robot Kangaroo. 6th Workshop on Legged Robots during the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2022), May 2022, Philadelphie, PA, United States. ⟨hal-03669855v2⟩
[5] Y. Sugahara, T. Hosobata, Y. Mikuriya, H. Sunazuka, Hun-ok Lim and A. Takanishi, « Realization of dynamic human-carrying walking by a biped locomotor, » IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2004. Proceedings. ICRA ’04. 2004, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2004, pp. 3055-3060 Vol.3, doi: 10.1109/ROBOT.2004.1307526
[6] K. G. Gim, J. Kim and K. Yamane, « Design and Fabrication of a Bipedal Robot Using Serial-Parallel Hybrid Leg Mechanism, » 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 2018, pp. 5095-5100, doi: 10.1109/IROS.2018.8594182
[7] Chignoli, Matthew, Donghyun Kim, Elijah Stanger-Jones, et Sangbae Kim. « The MIT Humanoid Robot: Design, Motion Planning, and Control For Acrobatic Behaviors ». In 2020 IEEE-RAS 20th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), 1‑8. Munich, Germany: IEEE, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/HUMANOIDS47582.2021.9555782
[8]Grimes, Jesse A., et Jonathan W. Hurst. « THE DESIGN OF ATRIAS 1.0 A UNIQUE MONOPOD, HOPPING ROBOT ». In Adaptive Mobile Robotics, par A K M Azad, N J Cowan, M O Tokhi, G S Virk, et R D Eastman, 548‑54. WORLD SCIENTIFIC, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789814415958_0071
[9]Fadini, G., T. Flayols, A. Del Prete, N. Mansard, et P. Soueres. « Computational Design of Energy-Efficient Legged Robots: Optimizing for Size and Actuators ». In 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 9898‑9904. Xi’an, China: IEEE, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA48506.2021.9560988
[10]Qu, Zhanghao, Peng Zhang, Yaohua Hu, Huanbo Yang, Taifeng Guo, Kaili Zhang, et Junchang Zhang. « Optimal Design of Agricultural Mobile Robot Suspension System Based on NSGA-III and TOPSIS ». Agriculture 13, no 1 (14 janvier 2023): 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010207
De plus, le travail s’appuie également sur l’ensemble des références suivantes :
FANKHAUSER, Péter et HUTTER, Marco. ANYmal: a unique quadruped robot conquering harsh environments.
Research Features, 2018 – En savoir plus
KATZ, Benjamin, DI CARLO, Jared, et KIM, Sangbae. Mini cheetah: A platform for pushing the limits of dynamic quadruped control. In ICRA 2019 – En savoir plus
GRIMMINGER, Felix, MEDURI, Avadesh, et al. An open torque-controlled modular robot architecture for legged locomotion research. IEEE RAL, 2020 – En savoir plus
MASTALLI, Carlos, BUDHIRAJA, Rohan, et al. Crocoddyl: An efficient and versatile framework for multi-contact optimal control. In IEEE ICRA, 2020 – En savoir plus
Nelson, Gabe, Saunders, Aaaron, Playter, Robert (2019). The petman and atlas robots at boston dynamics. Humanoid Robotics: A Reference, 169, 186. En savoir plus
Hurst, J. (2019). Walk this way: To be useful around people, robots need to learn how to move like we do. IEEE Spectrum. En savoir plus
STASSE, Olivier, FLAYOLS, Thomas, et al. TALOS: A new humanoid research platform targeted for industrial applications. In IEEE Humanoids 2017
CARPENTIER, Justin, SAUREL, Guilhem, et al. The Pinocchio C++ library. In IEEE SII, 2019
VULLIEZ, Margot, ZEGHLOUL, Said, et KHATIB, Oussama. Design strategy and issues of the Delthaptic, a new 6-DOF parallel haptic device. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2018. En savoir plus
CHADWICK, Michael, KOLVENBACH, Hendrik, DUBOIS et al. Vitruvio: An Open-Source Leg Design Optimization Toolbox. IEEE RAL 2020. En savoir plus
FADINI, Gabriele, FLAYOLS, Thomas et al. Compu- -tational design of energy-efficient legged robots: optimizing for size and actuators. In ICRA 2021. En savoir plus
SEMASINGHE, Chathura, TAYLOR, Drake, et REZAZADEH, Siavash. A Unified Optimization Framework and New Set of Performance Metrics for Robot Leg Design. In IEEE CRA 2021. DOI: 10.1109/ICRA48506.2021.9561618
AKKARI A. C. S., DA ROCHA M. F. M. et DE FARIAS NOVAES R. F. Cognitive ergonomics and the industry 4.0. Brazilian Technology Symposium, 2017, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-93112-8_28
SCHNEIDER E. et IRASTORZA X. Work-related musculoskeletal disorders. European Agency for Safety and Health at Work (EU-OSHA), 2010. En savoir plus
MAURICE P., PADOIS V., MEASSON Y. et BIDAUD P. Human-oriented design of collaborative robots, Int. Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2017. En savoir plus
Alliance Industrie du Futur, Le guide des technologies de l’industrie du futur, 2018. En savoir plus